Diabetes screening
Diabetes is a disease that happens when your blood sugar is too high. We’ll cover what you need to know about diabetes causes, symptoms, who’s at risk, how MinuteClinic® can help you get screened and what types of diabetes are preventable.
Find care
We offer services at MinuteClinic

Insurance and pricing
Most insurance accepted. Check your coverage or estimate the cost of your visit if you’re uninsured or prefer to pay out-of-pocket.
Have questions about getting screened for diabetes? Here are the basics.
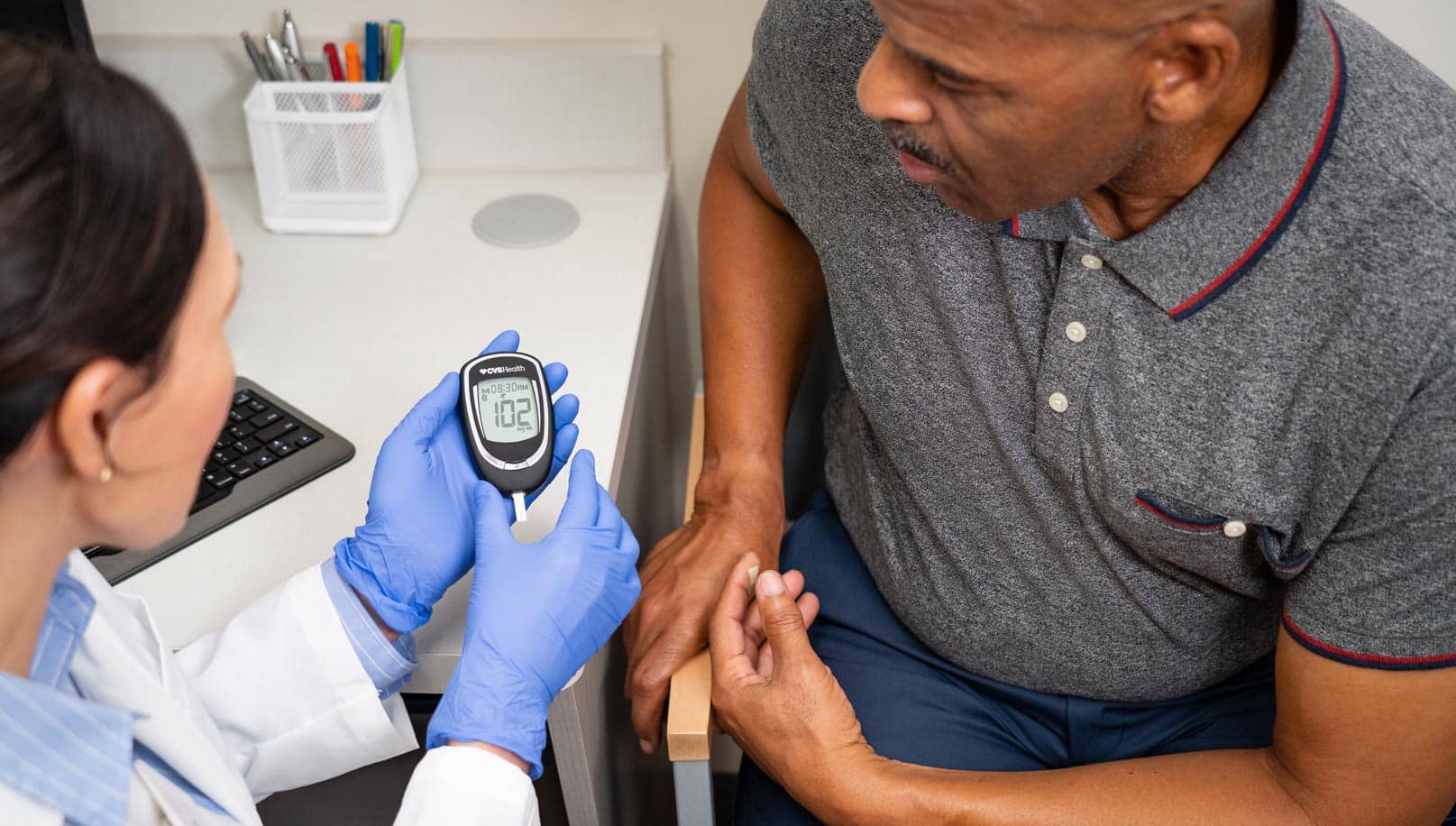
What is diabetes?
Diabetes (diabetes mellitus) is a class of metabolic diseases marked by high blood sugar (hyperglycemia). High blood glucose can increase the risk of developing a condition known as prediabetes, type 2 diabetes itself and diabetes complications. A glucose screening is a blood test that measures the glucose level in your body.
What is prediabetes?
Prediabetes is the condition when blood glucose levels are higher than normal but not so high as to be diagnosed as type 2 diabetes. Prediabetes puts you at a high risk of developing type 2 diabetes and the complications of diabetes such as cardiovascular disease. According to the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), approximately 84 million American adults (more than 1 out of 3) may have prediabetes. Of those with prediabetes, 90% do not know they have it.
Who should get screened for diabetes?
Since diabetes symptoms can often go unnoticed, health care providers recommend regular screening tests for:
- Anybody with symptoms of diabetes
- Anybody with risk factors such as being overweight or having a history of diabetes in the family
- Children and teens ages 10 through 18 with the following risk factors:
- Are overweight
- Had a low birth weight
- Their parent had diabetes while pregnant
When should diabetes screening tests be done?
Screening is necessary if you’ve noticed any symptoms associated with diabetes. Some people might not experience any symptoms but could be at risk for diabetes because they have:
- High blood pressure: This is measured as equal to or greater than 140/90 in adults
- Abnormal cholesterol: High cholesterol levels could be an indicator of diabetes or prediabetes
- Being overweight or obese: A body mass index (BMI) of 25 or above may be a risk factor for diabetes
- Family history of diabetes: Screening is necessary if you have parents or siblings with diabetes
Diabetes testing allows diabetes or prediabetes to be discovered so that you can begin treatment, manage the condition and prevent complications.
Getting help
MinuteClinic providers can administer type 2 diabetes screening tests and perform examinations. They can review and help you understand the key health indicators from the test results. They can also make treatment recommendations.
- Prior to scheduling your appointment, you may have to answer a few questions about symptoms to help us prepare for your visit.
- Check-in varies depending on how you scheduled your appointment:
If you made your appointment online:
Check in using the email or text message we sent to confirm your appointment. If you prefer to check in using the electronic kiosk, make sure you have your confirmation code.
If you made your appointment in the clinic:
Sign in at the electronic kiosk.
- When it's time for your appointment, a provider will call your name.
- Your provider will conduct a thorough examination based on your reason for visit, presenting symptoms and health history. Charges will be based on examination and services provided during the visit.
- At the end of your visit, you are provided with a visit summary, receipt and educational material about your diagnosis. At your request, we can send your primary care provider information about your visit.
Diabetes causes, screening and symptoms
A MinuteClinic® provider will give you an FPG (fasting plasma glucose) test to measure the blood glucose level at a single point in time. For the most reliable results, FPG testing usually happens in the morning, after you fast by not eating or drinking anything for at least 8 hours. Your MinuteClinic provider will take a blood sample from your finger to test your blood glucose. If you are not fasting, MinuteClinic providers can also diagnose diabetes with a random blood sugar or A1C (glycated hemoglobin) test.
Diabetes screening allows prediabetes or diabetes to be discovered sooner. It lets you get early treatment, manage the condition and prevent more serious health issues.
Both Type 1 diabetes and Type 2 diabetes are believed to be genetic conditions with one or both parents contributing to risk factors. This means if one or both parents have Type 1, a child of those parents needs diabetes testing from because the disease often arises in childhood. Type 2 diabetes typically takes longer to develop. This is because it mainly occurs due to lifestyle factors. You may have risk factors for the disease and never develop it if you maintain a healthy diet and exercise plan.
Causes of Type 1 diabetes
- Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the cells that produce insulin. The medical community doesn't know what causes Type 1 diabetes, but they think that genes or environmental factors, such as viruses, might trigger the disease.
Causes of Type 2 diabetes
Type 2 diabetes develops over the course of many years and is caused by several factors including:
- Obesity (being overweight)
- Lack of physical activity
- Poor nutrition
- Genes & family history
- Excessive thirst and dry mouth
- Sudden weight loss
- Frequent urination
- Extreme fatigue or lack of energy
- Constant hunger
- Blurred vision
- Numbness in hands and feet
- Slow-healing wounds
Symptoms of type 1 diabetes can start quickly — even in a matter of weeks. Symptoms of type 2 diabetes often develop over time and can be so mild that you might not even notice them.
Type 1 diabetes (insulin-dependent diabetes) used to be called juvenile-onset diabetes because it usually begins in childhood. Type 1 diabetes involves insulin therapy.
Currently, there is no evidence of interventions that can prevent or delay the onset of type 1 diabetes, so routine screening for type 1 diabetes is generally not recommended. MinuteClinic® providers do not manage type 1 diabetes.
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes. Often, no symptoms appear in the early stages. For this reason, it may not be diagnosed for many years. People with no diagnosis and treatment of type 2 diabetes are at risk of chronic hyperglycemia. It is a condition associated with long-term damage to the eyes, kidneys, nerves, heart and blood vessels.
Early diabetes screening tests can help people avoid the more severe complications of the disease. There is also a greater likelihood of abnormal cholesterol, high blood pressure and obesity in individuals with diabetes. At present, no cure exists for type 2 diabetes. However, medical treatment, weight management, nutrition and exercise can reduce its effects.
Diabetes prevention
Type 1 diabetes isn’t preventable. Your primary care provider can help you manage type 1 diabetes with treatment. You may avoid or delay the onset of type 2 diabetes by improving your diet and getting more exercise. Health care providers recommend 30 minutes of exercise 5 days a week to help avoid type 2 diabetes. Quitting smoking may also make a big impact on diabetes prevention.
Weight-loss programs as well as changes you can make to your diet, including adding more nonstarchy vegetables such as asparagus, broccoli and peppers. Lean protein, fruits and whole grains may also help with prevention. You can also replace sodas and sugary drinks with water or unsweetened beverages. Compounded GLP-1 and controlled substance medications for weight-loss are not prescribed at MinuteClinic® (includes Phentermine, among others).
IMPORTANT! PLEASE READ: This material is for reference only and should not be used to determine treatment for specific medical conditions. Please visit a health care provider for evaluation, diagnosis and treatment of any symptoms you may be experiencing. If you're experiencing a medical emergency, please dial 911 or visit your local emergency department.
REFERENCES USED AS SOURCES FOR THIS PAGE:
-
1. Type 2 Diabetes Screening, Testing, and Diagnosis via WebMD. (Accessed 3rd January 2024)
-
2. Types of Diabetes Mellitus via WebMD. (Accessed 3rd January 2024)
-
3. Diabetes Tests & Diagnosis via NIDDK. (Accessed 3rd January 2024)
-
4. Screening for Diabetes in Adults via Diabetes Canada. (Accessed 3rd January 2024)
-
5. Genetics of Diabetes via American Diabetes Association. (Accessed 1st February 2024)
-
6. Prevent Type 2 Diabetes via CDC. (Accessed 1st February 2024)
-
7. Exercise and Type 2 Diabetes via National Library of Medicine. (Accessed 1st February 2024)
-
8. Reduction in the Incidence of Type 2 Diabetes With Lifestyle Intervention or Metformin via National Library of Medicine. (Accessed 1st February 2024)